GitHub Basics
Keywords
- clone - Copy a repository from GitHub to your local machine
- branch - A version of the code that deviates from the branch it originated from
- Pull Request - A request to merge one branch into another
- conflict - When git cannot resolve a merge without manual intervention
Concepts
GitHub is a place to store repositories, share them with other GitHub users, and collaborate with others on projects. GitHub involves the Git installed on your computer to host a local version of the repository on your computer. When you have committed changes you will push your commit history (think upload) to the GitHub platform.
Multiple Branch Git History
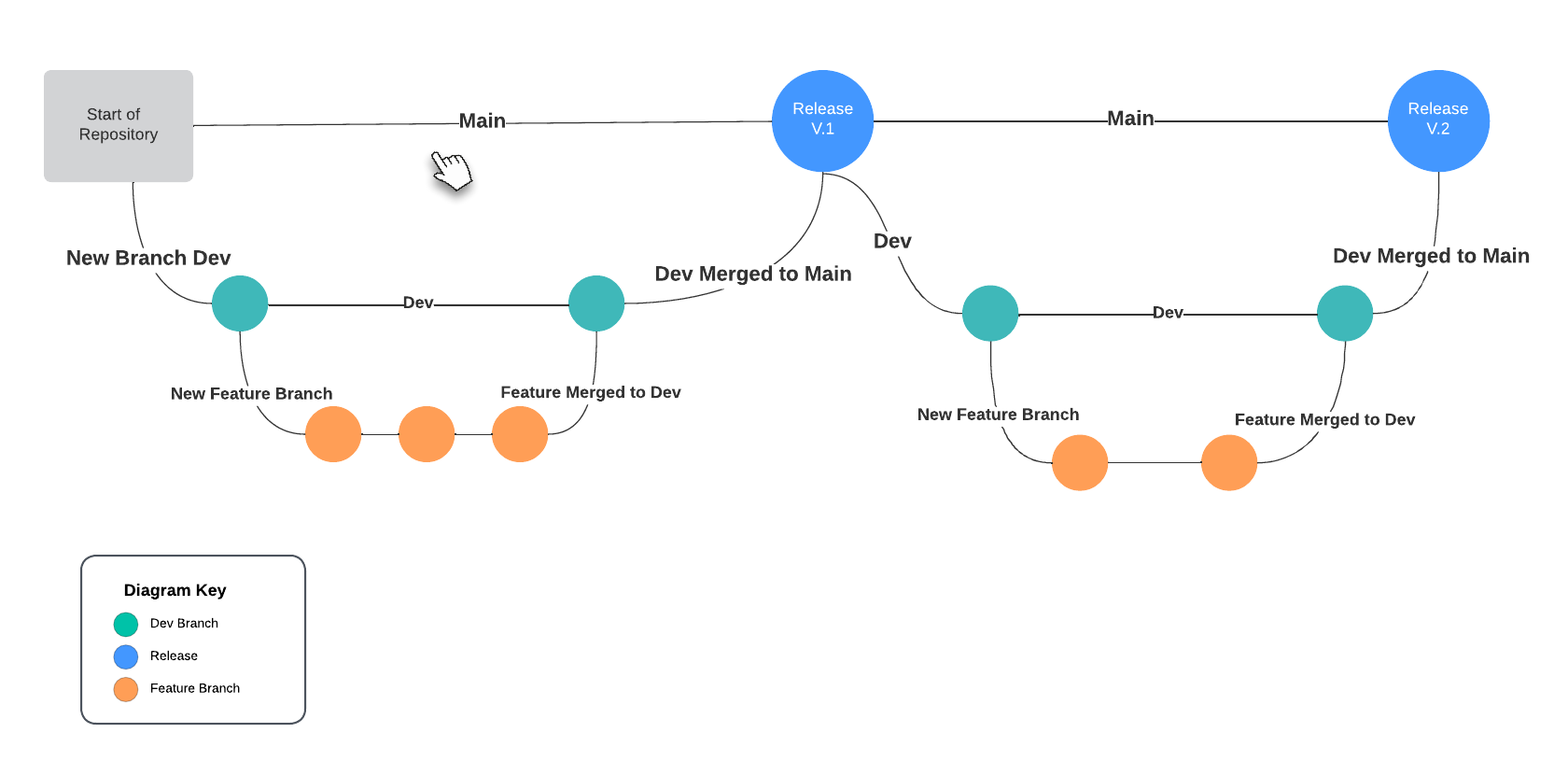
Create a Repository on GitHub and Push a Commit
Login to GitHub then create a new repository

and give it a name, or use the suggested name, then select the option to add a README.md. After the repository has been created navigate to the drop-down seen below
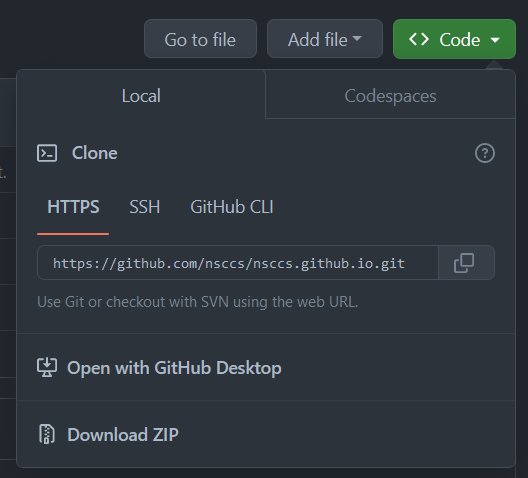
Copy the link to the clipboard and return to a terminal and type
git clone https://github.com/username/repository
A new repository now exists. Change directories into the new repository and open it in your text editor/IDE of choice.
Now the same commands used for Git that were covered previously may be used to track changes within this repository. However, it is time to introduce the concept of a branch.
git checkout -b new-feature
As long as you don't change anything on this branch you can switch back to the main branch with
git checkout main
then switch back
git checkout new-feature
However, once changes are made within your new-feature branch you may not switch to other branches without first committing those changes.
Make some changes to your readme and commit them. Now to upload these changes to the remote repository you will push the changes with the git command line tool.
git push origin new-feature
You have successfully uploaded your code and commit history to the remote repository!
The Pull Request
The last piece of the puzzle is the Pull Request. Could you have done the above steps directly on the main branch? Yup, but it is generally frowned upon and most repositories you will encounter in the wild will have restrictions that do not allow directly pushing to main.
A Pull Request is an intermediary step that allows you and the people you collaborate with a chance to review your work, test it, and offer constructive feedback. Changes might be requested before the new feature can be merged into the main codebase. There are other actions that can be configured at this stage that are out of scope for this workshop.
Navigate back to your remote repository in the browser and select the Pull requests option from the tabs that start at the left.

Press the big green button that says New pull request and you will be presented with two dropdown menus. On the left is the branch you want to merge your work into and the right is your feature branch.
Select main on the left dropdown and new-feature on the right. Then click the green button to create the pull request.
Basic Git Commands Used with GitHub
git checkout -b <new-branch-name> Create a new branch
git checkout <existing-branch-name> Switch to an existing branch
git add <file_name> Add file to commit (stage it)
git commit -m "<message>" Commit files with clear message about commit
git push <remote> <branch> Push locally saved commits to a remote
git pull <remote> <branch> Pull latest state of repository for selected branch
Conflicts
The above layout describes scenarios where everything goes well. There are often scenarios where this does not occur. One of the most common issues that arises is when more than one person work on a single document. Person A and Person B create their own new branches off of the main branch. Both Person A and Person B will work with Document C. Person A finishes their work and submits a PR which is approved and merged into main. Then Person B does the same. At this point Document C in main has been changed since Person B originally created their branch. Person B's PR will have a conflict, and it will need to be resolved manually.
Merge Conflict Git History
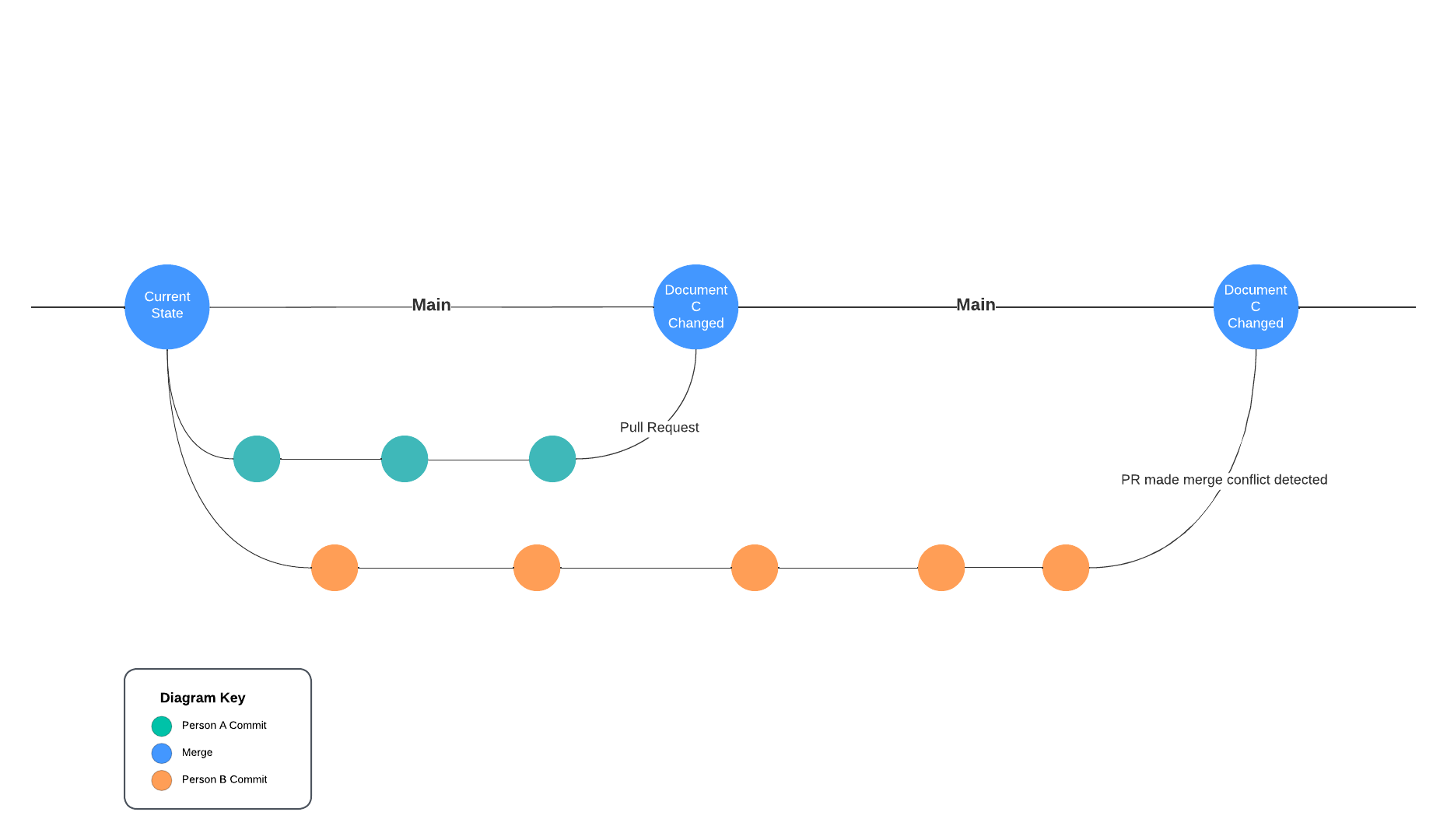
There are various ways to solve merge conflicts within GitHub's platform as well as locally. Reach out for help, search the web, and don't panic!